How 3D Printing is set to transform India’s Manufacturing Sector
Dec 4, 2021

The Indian manufacturing industry is one of the most rapidly expanding industries in the world. Over the forecast period (2021–2030), the need for mass customization in goods has risen significantly. 3D printed applications are seeing a boom in India’s automobile, defense, aerospace, and aviation sectors. All these factors will help to fuel the development of the 3D printing market.
Due to increased customizability and a reduction in errors, zero-material waste, low development costs & time, 3D printing has become a major market focus in recent years.
In the aerospace sector, the growing need for 3D printed high-performance polymers is one of the most important factors driving market development. The explosion in demand for aircraft to transport more cargo and people has increased the demand for light-weight aviation components. This has resulted in increased use of additive manufacturing in aircraft components.
“India has seen increasing adoption of 3D printing technologies with growth rates over 30% year-on-year across materials. The industry has evolved from being a prototyping tech to end use production, with metal AM (additive manufacturing) leading the course.”
– Mahesh Makhija, Partner, Technology Consulting, EY.
Furthermore, the growing production base of the robotics, medical prosthesis, and automotive sectors in India will accelerate the market’s expansion in the future. Today, 3D printing is extensively used in a variety of industries, including consumer electronics, military, aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and education, to name just a few. It is critical to take the big picture into consideration.
In our discourse, we will talk about the following —
- History of 3D printing in India
- Present-day status of 3D printing in India
- Real-life examples: Cementing the presence of India in 3D printing
History of 3D printing in India
It is unclear how and when 3D printing entered the Indian market. However, we can trace its roots in history by looking at companies that are well established and have been in this field for a significant period. Over a decade ago, the cost of 3D printers ranged from Rs. 40,000 to Rs. 2 lakhs. These printers were beginner-level models popular in the US and Europe. They were often sold as DIY kits.
Shiny beginnings
The 3D printing story in India is incomplete without mentioning “Imaginarium”. It is a Mumbai-based company that was founded in 2003. It was using 3D printing to make jewelry. They managed to reduce waste and cut costs in jewelry production. It also improved their turn-around time. In the year 2006, they started another specialized engineering branch called Rapid which views 3D printing from a manufacturing lens.
The medical field is one of the fastest industries to take up new technology. Therefore in 2011 Imaginarium used 3D printing to help doctors with medical solutions. Eventually, they started to provide 3D printing services in various sectors like architecture, construction, automotive, and consumer goods.

In 2012, four friends at an incubator program in Manipal University started a 3D printing business calledGlobal 3D Labs (2014). Their focus was on manufacturing, sales, and servicing 3D printers. They developed their own 3D printers for hobbyists and the baking industry. Fabheads, started in 2015, took 3D printing to a new level by developing Carbon Fiber 3D printing process. Today, many other companies like divideByZero, Ethereum have also come up in Indian 3D printing arena.
Present-day status of 3D printing in India
In their respective fields, some of the finest Indian-based 3D Printing businesses have shown their mettle. They are using a range of methods in order to innovate the 3D Printing market.
Government Organisations
In recent months, the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) inked formal Memorandums of Understanding with Agnikul Cosmos and Skyroot Aerospace. They received access to ISRO’s resources and experience in building and testing space launch vehicles. ISRO is also experimenting with fiber printing for its space worthy components.
The Defense Research and Development Organization has certified a key aero engine component that was produced by Wipro 3D and Hindustan Aeronautics Ltd.
Along with DRDO and ISRO, Indian Army, Indian Navy and Indian Air Force are looking to establish their own centers for 3D printing, where they can produce required parts, as well as, do further research on this technology.
Private Organizations
Fabheads, another organization specializing in the composites manufacturing industry, was the first company in Asia to develop in-house fibre 3D printing capabilities. It has won many accolades including the prestigious iDEX award to develop Carbon fiber Helicopter blades for Indian Air Force. Fabheads also won National Startup of the year 2020, a first for a 3D printing company.
DivideByZero became the first Indian company to sell their in-house developed 3D printer to USA. Tvasta is the first 3D printing construction company in India. We will look at these companies in detail in following sections.
In early 2021, L&T Construction achieved success in 3D printing the world’s first two-story structure, which was created using a unique concrete mix.
Type of 3D printer companies
At present, 3D printing can be divided into the following types of business models —
- 3D printer developers — Design and Development in-house (Fabheads, Objectify Technologies and Fracktal Works)
- 3D printer re-sellers — Companies re-selling 3D printers made in India or other countries (Novabeans, 3D Print World and Time to 3D)
- 3D printing services company — Providing manufacturing services using 3D printers (Fabheads, Objectify Technologies, Stratasys India and Fracktal Works)
While re-sellers and service companies are a big part of the 3D printing eco-system, it is the rise of 3D printer development companies in India which really shows the huge strides India has taken in the field in recent years.
“In case of carbon fiber, by actually using additive manufacturing, you can increase the strength of the material. So you can tweak the processes, tweak the overall mass and weight of the system and even the strength. So that is how this material is actually the most ideal candidate for additive manufacturing. ”
— Dhinesh Kanagaraj, CEO of Fabheads Automation
3D printing growth in India
The interest in 3D printing is growing in our country. Researchers are exploring 3D printing technology to solve a wide range of problems. ‘A Study on The Entrepreneurial Opportunities, Global and Indian Economy in 3D Printing Sector’ dives deep into the impact of 3D printing on our Indian sector. Also, we can evaluate the growth of 3D printing adoption in India by looking at some graphical representations of data given below. From the data, we can infer that the growth of 3D printing in India is slow but steady.
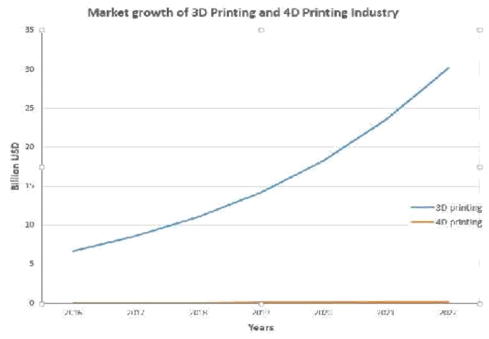
UditMistry207 Licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0]
Real life examples: Cementing the presence of India in 3D printing
Industry 4.0 promises digitization of the manufacturing industry. It is a huge opportunity to go full-throttle into this venture using 3D printing. Digital fabrication or manufacturing use rapid prototyping and on-demand manufacturing to speed up the rate of production. At the same time, it serves to make customer-centric products. Using 3D printing India can expand economic growth and improve employment across the different fields. Let’s look at some startups and companies that are investing in these sectors
Aerospace & Defense
India is on the path to become a major exporter of defense equipment. The A&D industry has been using 3D printing since 1989. Using 3D printing it can achieve the following—
- Lightweight parts
- Functional & practical prototypes (Rapid prototyping)
- Low-volume production
- Material efficiency
Indian companies have also made significant progress in this field.
Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) — Recently, the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) signed off on MoUs with Skyroot Aerospace and Agnikul Cosmos. This provides them access to ISRO’s facilities and expertise in the development and testing of space launch vehicles. System and subsystem testing and development for space launch vehicles will take place at ISRO facilities. This will be used by the two start-ups.
ideaForge — In the past, when we talked about advanced defence technology, we frequently resorted to foreign corporations for guidance. The present situation, on the other hand, is very different. The rise of companies such as ideaForge and Fabheads has resulted in a reversal of trends, with world-beating technology being developed right here in India.
ideaForge is the world’s biggest producer of drones for use in defence, homeland security, and industrial purposes, and it is headquartered in India. A highly integrated company with in-house R&D, design, software, production, services, and training activities, as well as manufacturing and services.
ideaForge was successful in securing a lucrative contract with the Indian Army to provide drones worth Rs. 145 crores ($20 million). In terms of the military, this is a major step forward in the direction of’modernization.’
The Indian Army placed an order with an Indian firm, ideaForge, for an upgraded version of SWITCH tactical drones. These are specialised drones that are designed to fly at high altitudes, such as those seen in Ladakh.
Agnikul Cosmos — It is a startup that was founded in 2017. They work on building small satellite launch vehicles. They are building rockets with a capability of 100 kg payload. The rocket’s engine is 3D printed in one run! Typically, a single rocket engine has more than 100 tiny components. This is the first time that any company has developed a semi-cryogenic fully 3D printed rocket engine.
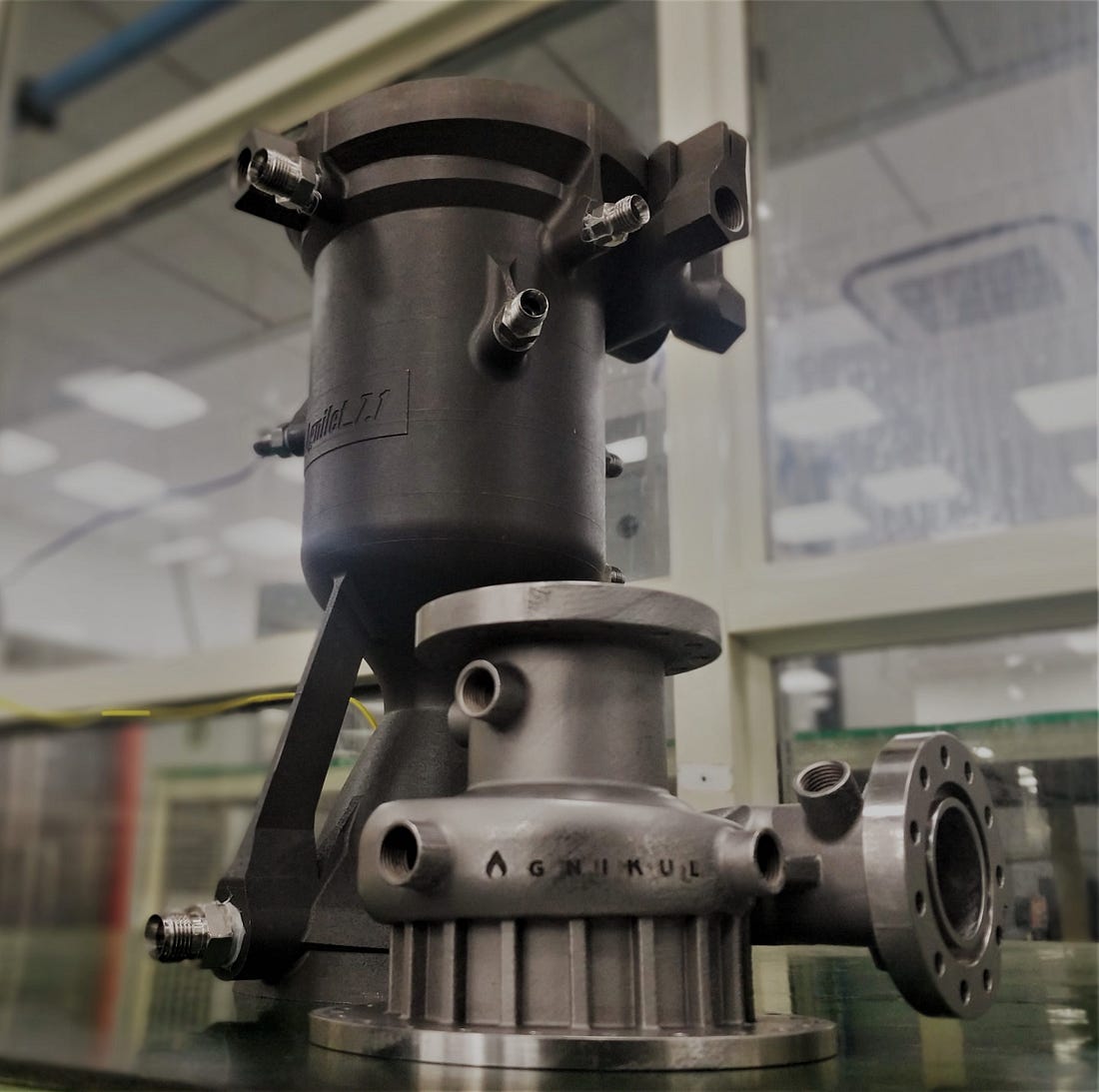

“Over the next few years, I expect Engineering, Industrials, Tooling, Education, Medical and Aerospace & Defense segments should exhibit promising growth in India’s 3D printing market.”
– Santosh Kasture , Director of Fast Track Management Consultants
Fabheads — It is a composite manufacturing company that works with hybrid manufacturing techniques. 3D printing is a prominent addition. Fabheads is the first and only organisation in India to have developed a Carbon fiber 3D printer. This is a feat which only a handful of companies around the world have achieved.

Why Carbon Fiber? — Carbon fiber composite is twice as strong as steel but 5 times lighter, making it the ideal manufacturing material for many aerospace parts. (Read more about it in our article on carbon fiber)
Fabheads caters to several industries like automotive, aerospace, shipping etc. The composite 3D printing technology has been used in several drones, marine products, etc. Fabheads is set to launch their printers in the market in late 2021, with target customers ranging from DIY enthusiasts to aerospace companies.
Automobile Sector
Additive manufacturing services are extensively used in the automotive industry. With an influx of new automotive designs entering the market, it is critical for designers and other stakeholders to verify new ideas via the use of visual models. It doesn’t matter if it’s a tiny tabletop visual model or a full-sized car model.
For example, in one case that was brought up, Imaginarium managed to 3D print components for a manufacturer who was building a supercar for a show in the United Kingdom using 3D printing technology. A large number of the components, including the headlight, black hood, tyres, air vents, wings, and the logo, were said to have been created using 3D printing technology. It has been said that 3D printing is capable of producing translucent or opaque components for painting elegant visual representations in addition to materials and finishes.
“In the coming era it is going to be mass customisation over mass manufacturing in the automotive segment.”
— Director, Imaginarium (India) Pvt. Ltd.
The use of the following techniques in the automotive industry make 3D printing the skeletal system of automobile manufacturing —
- Generative design
- Optimisation of style & topology
- Customization of parts and components
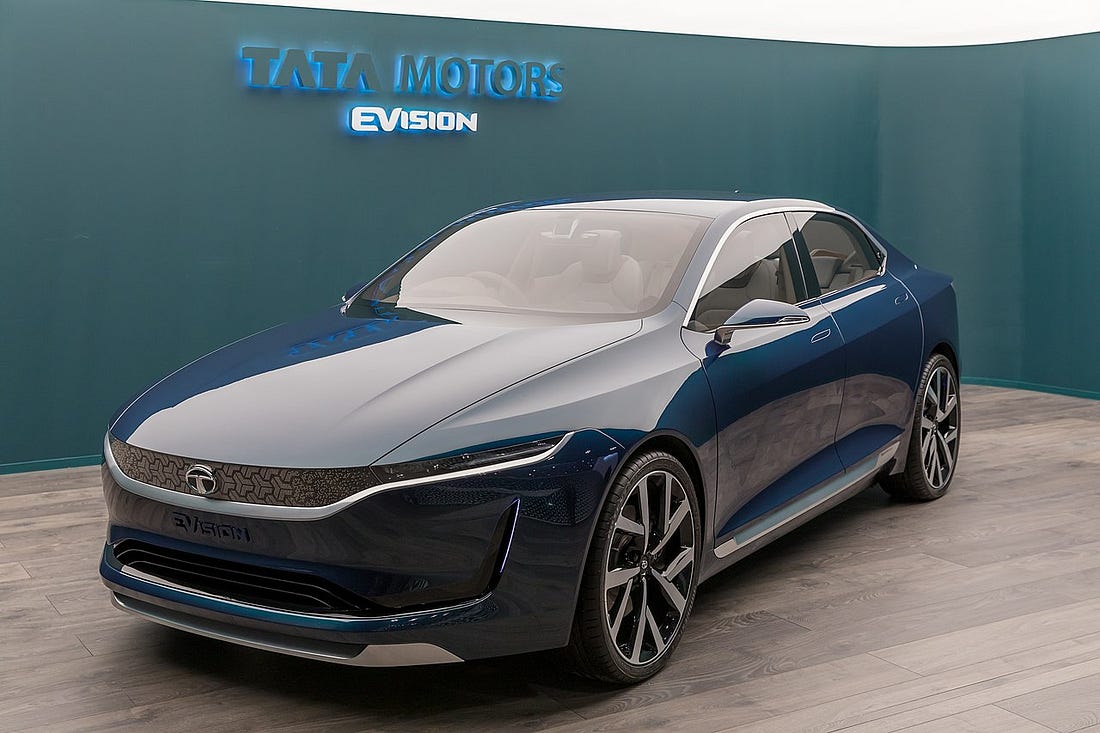

Tata Motorsand Maruti Suzuki are two top automobile companies that have invested in R&D for the 3D printing of cars.
“3D printing is an integral part of our production process. We are running several internal initiatives around this technology, which involve designing select parts of the vehicle that are 3D-printed.”
— Pratap Bose, head of design, Tata Motors.
In July 2021, Tata Technologiespartnered with Stratasys to enable additive manufacturing in India. Stratasys will help with its expertise and knowledge on 3D printing to give automotive (and other) solutions in the manufacturing landscape of India. Check out this article to know more.
Medical
The Medical & dental sectors are also realizing the potential of 3D printing. Bio-printing has revolutionized the medical industry. From building prosthetics to growing live tissues, 3D printing has versatile and diverse applications in Medicine. With the help of AM, one can now create implants, grow cell cultures, make dental dentures and much more.
This is an area in which Indian companies have also achieved significant success in recent years.
AlgoSurg — AlgoSurg group is focused on Algorithms for 3D Simulation of Orthopedic Surgeries for a variety of applications ranging from augmented reality-based surgical navigation and robotics to automatic patient-specific instrument/implant design (X3DPSI), cloud-based 3D surgery planning (Tabplan3D), and augmented reality-based surgical training and education (OpenSurgiSim).
“We need disruptive innovations in Healthcare Technology.”
Vikas Karade, AlgoSurg CEO
‘XrayTo3D’ is the term given to the technology that allows two-dimensional X-ray pictures to be converted into three-dimensional models. Tabplan3D is a piece of software created by Vikas Karade, the CEO of AlgoSurg and an IIT Bombay researcher. It may be used to design orthopaedic operations in a virtual 3D environment, which is quite useful. It will be helpful for joint operations such as deformity repair and joint replacements, among other things.
Divide By Zero — Divide By Zero has shown to be very beneficial to healthcare professionals both in India and across the world. Three-dimensional printing has made it possible to convert CT scans of the brain into models for mock surgery and anatomical models for research purposes. Their in-house Accucraft i250D printers have been used to produce pre-operative models for delicate and complex operations.
To assist medical professionals such as physicians and surgeons in planning, practising, and performing complicated and intricate operations, Divide By Zero offers a variety of resources to help them achieve more accuracy and better outcomes. A more application-based advantage is that medical schools and students may profit from the models that a 3D printer can produce, which can be used for research or practise reasons.
DBZ boasted of printers that created custom-made prostheses that were much more affordable, practical, and accurate than they were in the previous generation.
Architecture & Construction
3D printing is steadily making its way into the Indian construction industry, with both startups and big corporations introducing the technology to the country. 3D printers are being used in construction to build houses and buildings across the world. It uses materials like cement, concrete, plastic, polymers, etc. Construction using 3D printing is efficient and faster than traditional methods, taking up long hours of manual labour.
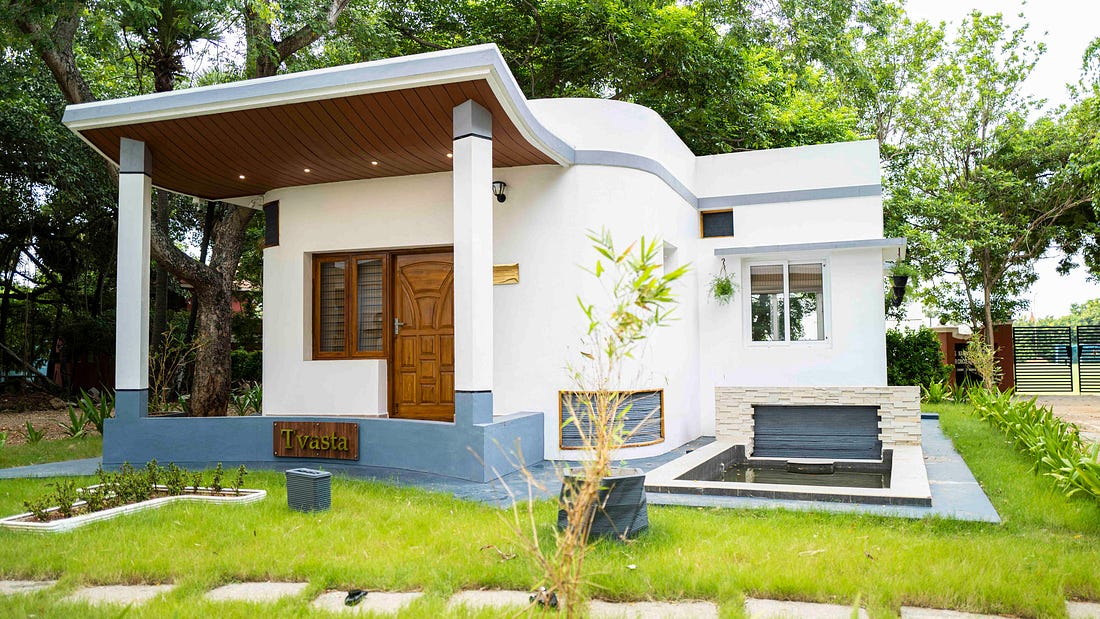
Tvasta, an IIT-M based start-up was able to construct a 600 sq. feet area house, using concrete 3D printing technology. Typically, a house of this size takes 4–5 months to complete. Thanks to 3D printing it just took 4–5 days.
This successful model paves the path for the construction industry. This technology can help optimize time, materials, and logistics. By 2022, it will be possible to build ~100 million houses.

L&T Construction has accomplished a significant milestone by building a 3D printed multi-storey residence, which the company believes will have a significant effect on the availability of cheap housing for the nation.
The structure, which has a small floor area of 65m², was manufactured utilising a large-format concrete 3D printer. It was constructed using a 3D printable real concrete mix that was created by L&T’s own team of architects and engineers. L&T’s building included vertical reinforcing bars and horizontal welded mesh distributors. The building was produced in a record-breaking 106 hours, which is a world record for 3D printing.
“3D printing will not only speed up the manufacturing of multi-floor constructions, but actually improve the quality and durability of houses.”
MV Satish, Senior executive vice-president at L&T Construction
The building, which is stationed at the Kanchipuram, in Chennai, features integrated reinforcing bars and is completely in agreement with all of India’s building regulations.
It is said that the creation of the 3D printed building is the first of its type in India and that it has the ability to significantly change affordable housing — both in terms of cost and in terms of the time it takes to create new homes.
These are only a few of many examples that tell the story of 3D printing in India. 3D printing will continue to grow and add to the global economy in future. It is not too ambitious to say that the future of 3D printing in India is bright. Many companies are shifting their focus from the traditional manufacturing space to AM. With companies like Relativity space (USA) 3D printing whole rockets, there is still a long way to go for Indian companies.
Learn more about these new Indian ventures in this article that has a list of top 3D printing startups in India.
Conclusion
Product development in India is becoming more popular. India is no longer just providing services through software but also inculcating the ‘design thinking’ approach to innovate and invent new products. 3D printing acts as a catalyst and enables people to research and use creative ways to construct or produce products that solve big problems.
India is only a few steps behind the global pioneers of 3D printing technology, but growing at a faster pace. The marketplace in India is diverse and unexplored to a large extent. This means that with the support of big companies and initiatives from the government, the future of 3D printing in India will become unstoppable.
“3D printing will introduce a new, leaner, Indian manufacturing industry”
— Anand Prakasam, Fortune India
Do you think 3D printing in India will help drive the “Make in India” initiative? Please share your thoughts in the comments below